
Start with the basics.
It’s midnight and Sam just finished work at the local hospital. As he walks out the door, he sees the bus pulling away from the bus stop (the worst). The next one won’t come for at least 30 minutes, so he takes a seat. About four miles away, Violet says goodbye to friends and sits at her bus stop. Checking the bus schedule, she sees the next bus isn’t supported to arrive for another 25 minutes! In fact, it’s the same bus that just missed Sam. Despite no other passengers in sight, the bus carries along on its regular route until it eventually reaches Violet — a bus that could have made for a happier Sam and a more efficient ride for Violet if they were able to request a ride and the bus ditch its route. Instead missed the mark on both. Whether it’s two passengers or 200, the bus always rides on the same route. How is this convenient or efficient? It’s not. Why can’t Sam and Violet just hail the bus like they hail a ride?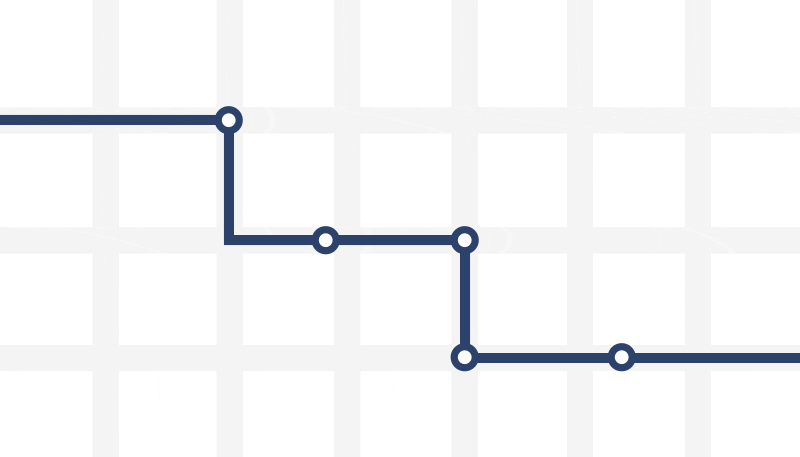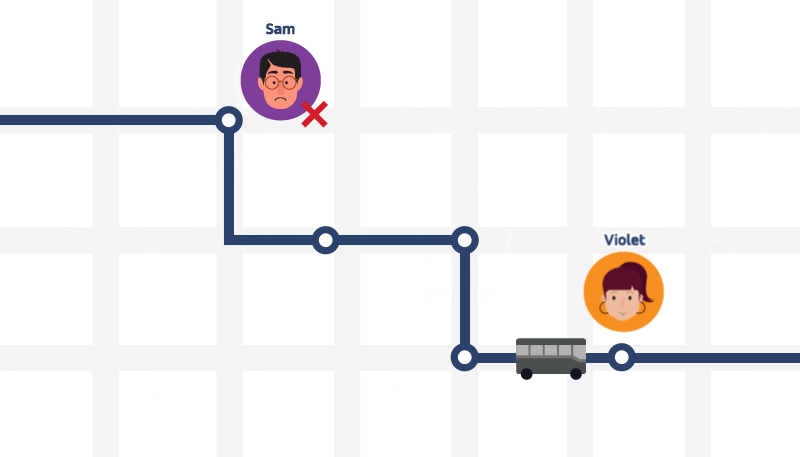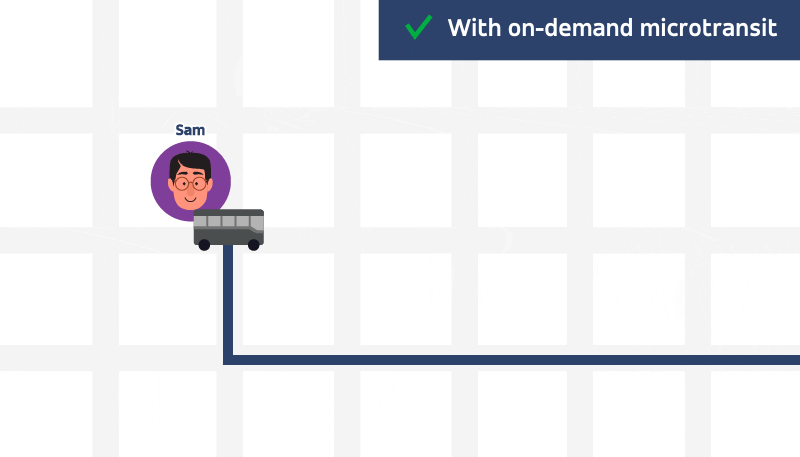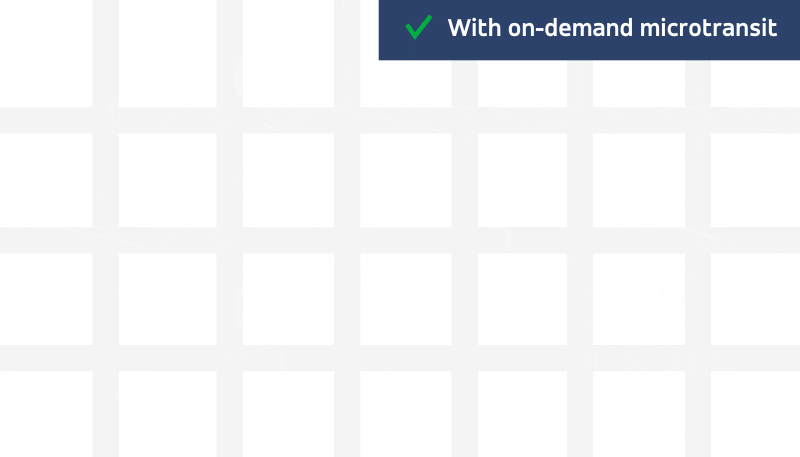 On-demand technology can dramatically improve the efficiencies of bus networks, especially during off-peak hours. Cities generally need fewer buses roaming the streets, and the ones serving rides are driving fewer miles, and serving way more passengers, who are waiting for a ride for far less time. It’s a win-win-win.
On-demand technology can dramatically improve the efficiencies of bus networks, especially during off-peak hours. Cities generally need fewer buses roaming the streets, and the ones serving rides are driving fewer miles, and serving way more passengers, who are waiting for a ride for far less time. It’s a win-win-win.
Seeing the model at scale.
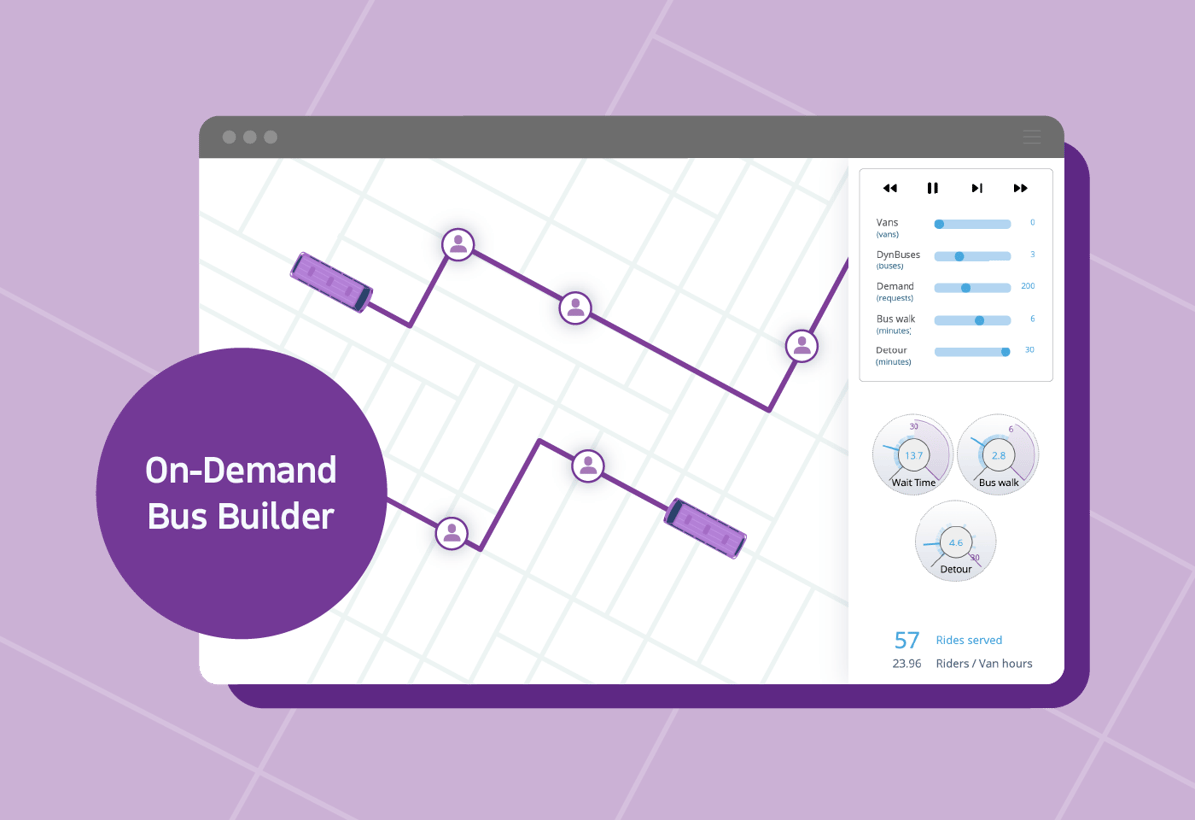
Now imagine the impact of dynamic bus routes across an entire city. Using the toy model below, you can see what a basic on-demand city bus network could look like at various supply and demand levels, with representative limits on detours, fleet size, and vehicle capacities. [via-sim-embed id="tool_3"]Your fleet, your rules.
- Supply: How many buses are in your fleet?
- Demand: How many requests do you expect potential riders to make? Does that number change based on time of day? Naturally, we want to be able to serve as many ride requests as possible.
- Bus walk: How many minutes do you think would be an acceptable walk time to a bus station?
So, how’d ya do?
Based on the choices you made when playing with the models, did you learn anything about how they affected the service? Here are a few things to consider:- Wait time: How long did passengers have to wait for a ride given the level of demand and number of vehicles in your fleet?
- Rides served: How many people who requested a ride were given an option that they accepted, and then completed?
- Utilization (rides per vehicle hour): How efficient was your use of vehicles?
.png?width=71&height=47&name=Sioux%20Falls%20Webinar%20(6).png)
%20(1)%20(1).png?width=71&height=47&name=Service%20Design%20Blog%20(2)%20(1)%20(1).png)

